The nature of consciousness has puzzled scientists, philosophers, and thinkers for centuries. While some schools of thought view consciousness as a mere byproduct of brain activity, others affirm its existence as a self-contained and singular phenomenon. Recent research has brought the Near-Death Experience (NDE) into the fold of consciousness exploration, challenging traditional views on the topic. NDEs, which are typically reported by those who have come close to death, offer a unique insight into the nature of consciousness and its relationship to the physical world. In this article, we’ll delve into the core components and after-effects of NDEs, examine traditional views of consciousness like Dualism and Materialism, look at how NDEs challenge these viewpoints, explore new perspectives on consciousness like Non-local Consciousness and Panpsychism, and discuss the potential implications and applications of this research.
Understanding NDEs

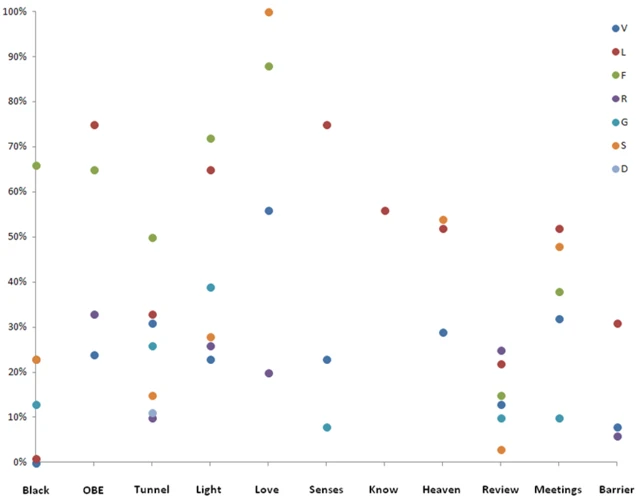
It is a perplexing and fascinating phenomenon that has puzzled scientists, philosophers, and the general public alike. Near-Death Experiences (NDEs) are subjective experiences that occur during a close brush with death, providing many common elements despite different cultural and religious beliefs. These experiences often include sensations of leaving the physical body, traveling through a tunnel, meeting with deceased loved ones, experiencing a life review, and encountering a bright light or a being of light. While NDEs defy easy explanation, they have been well-documented throughout history and continue to challenge traditional views of consciousness. Understanding NDEs is essential to explore the larger concept of human consciousness and its mysterious nature.
The Core Components of NDEs
During a near-death experience (NDE), people report a wide range of experiences, some of which go beyond the typical boundaries of human consciousness. The core components of an NDE include feelings of profound peace and well-being, out of body experiences, tunnel experiences, vivid memories of significant life events (both past and future), and encounters with beings of light or deceased loved ones.
These core components are often reported across different age groups, cultures, and religions, as described in studies on common elements of NDEs. They typically occur during moments of impending death or during medical trauma when the brain is deprived of oxygen or blood flow.
Despite the variability in the types of experiences people report having during NDEs, the core components remain consistent across populations. Each component is significant in its own way and is often described as a profound and transformative experience that can change the way people view life and death.
The After-Effects of NDEs
After experiencing a NDE, a person might undergo profound after-effects that may last for an extended period. These after-effects can be physical, psychological, and spiritual.
Physical after-effects: Some individuals who had a NDE reported experiencing changes in their sensory perception. For instance, colors might appear more vivid, sounds may seem louder, and smells may become more intense. Some NDErs have reported a heightened sensitivity to electrical and magnetic fields. Additionally, some NDErs may report feeling more energetic or more tired than usual.
Psychological after-effects: NDErs often describe feeling a significant shift in their mindset after their experience. They may become less materialistic, less fearful of death, and less concerned with their ego. They may also become more empathetic, understanding, and compassionate towards others. Some researchers suggest that these psychological changes might be due to a shift in their sense of self and their increased understanding of interconnectedness of all living beings.
Spiritual after-effects: NDEs can also bring about significant spiritual transformations in individuals. For some NDErs, the experience profoundly alters their belief systems and their understanding of the nature of the universe. They may become more spiritually attuned to their surroundings and have increased mystical experiences. Some NDErs even go through a “dark night of the soul,” where they experience an intense internal struggle as they try to integrate the profound spiritual experience into their daily lives.
It is important to note that not all individuals who experience a NDE will experience these after-effects. The cultural and religious beliefs of the person may also influence how they feel about the experience. For instance, individuals from cultures that place a higher value on the afterlife may have a more positive interpretation of their NDEs than individuals from more secular societies would. Additionally, the ethical implications of studying NDEs and the history of research surrounding the phenomenon are also essential factors to consider.
Traditional Views of Consciousness

The exploration of consciousness has puzzled scholars for centuries. Many philosophical and scientific traditions have offered explanations, but the issue remains unresolved. Two widely accepted views of consciousness are dualism and materialism. Dualism proposes that consciousness is a separate entity from the body, while materialism asserts that consciousness arises strictly from physical processes in the brain. However, near-death experiences (NDEs) have challenged these traditional views and led to new perspectives on consciousness. Before delving into these new perspectives, let’s first examine the traditional views of consciousness in detail. The history of NDEs plays a crucial role in understanding these traditional views.
Dualism
Dualism is a philosophical concept that separates the mind and body into two distinct entities. Rene Descartes, a French philosopher, introduced this concept and suggested that the mind is a non-physical substance that is separate from the physical body. This theory implies that consciousness, or the mind, is not directly connected to the brain or the body and can exist independently.
In the context of NDEs, dualism creates a challenge to traditional views of consciousness. When a person experiences an NDE, they report being able to observe their surroundings without the use of their physical senses. This suggests that consciousness can exist independently from the body, thus providing evidence for dualism.
However, dualism has been widely criticized for lacking scientific evidence and being difficult to prove. Materialists, for example, argue that if consciousness is separate from the brain and body, then it should be impossible to measure or observe. This is because our current understanding of science is based on the idea that physical matter can only interact with other physical matter.
Despite these criticisms, some philosophers and scientists continue to support the dualistic approach. They argue that consciousness cannot be explained solely by neural activity in the brain and that there must be some non-physical element to it.
It is important to note that cultural and religious beliefs also play a role in shaping opinions about dualism and NDEs. Some cultures and religions view the mind and body as separate entities, while others view them as interconnected. This can influence how NDEs and dualism are perceived and interpreted.
Ultimately, the debate over dualism and its relationship to NDEs highlights the complexity of understanding consciousness and the limits of our current scientific knowledge.
Internal link: To better understand the scientific debates surrounding NDEs, read our article on neuroscience and NDEs.
Materialism
Materialism is a philosophy that suggests that everything in the universe can be explained in terms of physical matter and natural phenomena. According to this view, consciousness arises from complex brain activity alone and ceases to exist upon death. This perspective has dominated Western science for several decades, and many scientists argue that Near-Death Experiences (NDEs) are mere hallucinations, the result of neurons firing in the brain at the point of death.
Proponents of materialism believe that mental states and consciousness are purely physical phenomena, with no inherent spirituality or supernatural essence. They posit that subjective experiences, such as emotions or sensations, can be explained entirely in terms of brain activity and chemical reactions. This position has been questioned by NDE research, which shows that consciousness can transcend the limits of the physical body and the brain, leading to profound and spiritual experiences beyond the material world.
One argument against materialism is the existence of NDEs, which suggests that consciousness must be more than just physical activity in the brain, since many people report having conscious experiences during periods of clinical death when the brain is not functioning or is severely compromised. The experiences of those who have had an NDE are highly consistent, which indicates that they are not just the result of random brain activity but are instead linked to a deeper, universal reality that transcends the physical world.
Some NDE accounts involve encounters with deceased loved ones, encounters with a higher power, and viewing events in distant locations. These observations are difficult to explain solely with materialistic views.
While materialism has been dominant in Western science for many decades, NDE research has challenged this view and called for a more nuanced understanding of the nature of consciousness.
Link to /ethics-studying-near-death-experiences/
The Challenge of NDEs to Traditional Views of Consciousness
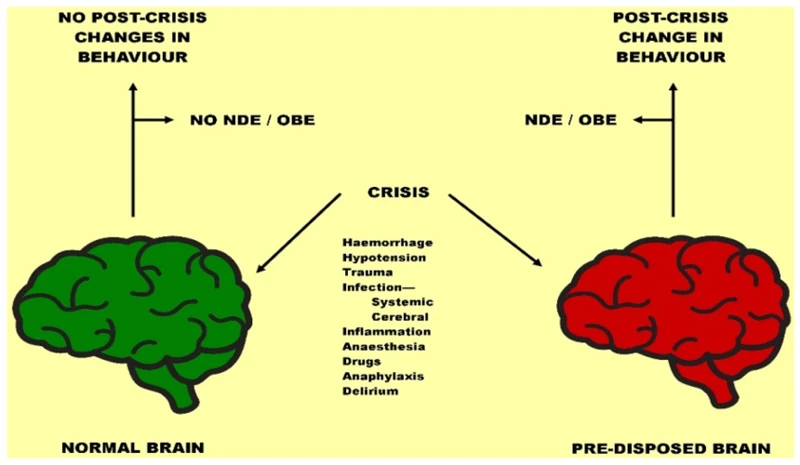
As we delve deeper into the understanding of near-death experiences, it becomes apparent that these profound events challenge our traditional views of consciousness. Dualism and materialism, two philosophical positions on consciousness, struggle to provide satisfactory explanations for the vivid and spiritual nature of NDEs. Despite the challenges, there are those who attempt to disprove the validity of NDEs or provide alternative explanations for them. Let us explore the challenge that NDEs pose to traditional views and the arguments that challenge NDEs’ credibility.
NDEs and Dualism
Near-Death Experiences (NDEs) pose a significant challenge to the traditional view of consciousness known as Dualism, which holds that the mind and body are separate entities. Dualists believe that consciousness exists independently of the brain and can survive the death of the physical body.
However, the vivid and lucid experiences reported by NDErs strongly suggest that consciousness is intricately connected to the brain. Many NDErs recall out-of-body experiences and interaction with deceased loved ones, which suggest a physical and material dimension to consciousness.
The cultural and religious beliefs of NDErs often shape their experiences, suggesting that consciousness is deeply intertwined with cultural and societal factors. For example, in some cultures, NDEs may involve encounters with deceased ancestors, while in others, NDEs may involve deities or religious figures. This suggests that the experience of consciousness is not universal, but rather shaped by cultural and religious factors.
Another challenge to dualism posed by NDEs is the fact that they often result in a profound transformation of the individual, suggesting that the mind and body are not separate, but rather deeply interconnected. Many NDErs report a loss of fear of death and an increased sense of empathy and connectedness with others.
In light of these challenges, some proponents of Dualism have modified their position to suggest that consciousness is both separate from and connected to the brain. However, the precise nature of this connection remains a subject of intense debate and research.
Internal link: the cultural and religious beliefs of NDErs often shape their experiences
NDEs and Materialism
Materialism is the philosophical view that suggests that everything in the universe, including consciousness, can be explained through physical matter and its interactions. Materialism, therefore, posits that consciousness is a byproduct of the physical brain, and that without the brain, there can be no consciousness. However, NDEs seem to challenge this notion of materialism.
During NDEs, many people report having experiences that go beyond what can be explained through physical matter. For example, some patients have reported having experiences of seeing deceased loved ones whom they had never met before or of meeting a “being of light” that emanated love and warmth. These experiences cannot be explained using a materialist framework alone since they do not involve any physical matter. Additionally, NDEs often result in profound transformations in the experiencer’s life after the event, which suggests that something beyond physical matter was involved.
Dr. Eben Alexander, a neurosurgeon who had a near-death experience, argues against materialism. He states that his NDE, which occurred when his brain was damaged and non-functional, challenged his previous beliefs in physicalism, which posits that consciousness arises from the physical processes of the brain. According to Dr. Alexander, his experience showed him that consciousness is not bound to the brain and that there exists an afterlife beyond the material world.
Psychologist Dr. David Fontana conducted a study in which he compared NDEs to hallucinations caused by drugs or lack of oxygen to the brain. However, he found that NDEs were fundamentally different from these other experiences. He discovered that NDEs are more vivid, more detailed, and more coherent than other hallucinations. These findings suggest that NDEs are not just random firings of neurons in the brain but are something more than that.
NDEs provide challenges to traditional materialist views of consciousness. They suggest that consciousness may exist beyond physical matter and that the brain may not be the sole source of consciousness. These experiences should be taken seriously and may provide valuable insight into the nature of consciousness and the afterlife.
Arguments Against the Challenges of NDEs
Despite the compelling evidence for NDEs challenging traditional views of consciousness, there are still arguments against these claims. Some skeptics argue that NDEs are simply the result of chemical and physiological changes in the brain during the dying process. According to this explanation, the brain releases large amounts of certain chemicals, like endorphins or ketamine, which can create feelings of euphoria, peace, or detachment. This chemical explanation is often used to discredit the spiritual or mystical interpretations of NDEs.
Another argument against the challenges of NDEs is the selective reporting of positive experiences. Some researchers suggest that the accounts of NDEs are biased towards positive stories because those are the ones people are more likely to share and remember. This argument suggests that there are just as many negative and distressing experiences during the dying process, but people may not be as willing to talk about them.
Finally, some argue that NDEs are simply the result of cultural conditioning or expectation. This argument suggests that people who have heard stories or beliefs about what happens after we die may be more likely to have experiences that reflect those cultural beliefs. Critics of this argument point out that similar NDEs have been reported across different cultures and belief systems.
Despite these criticisms, it is important to note that the accounts of NDEs are often consistent and significant changes in worldview and behavior are reported after these experiences. While the explanations for NDEs may be debated, the fact that they challenge traditional views of consciousness and have important implications for individuals and society cannot be ignored. To better understand the significance of NDEs, it is important to explore new perspectives on consciousness and continue research in the field.
New Perspectives on Consciousness

As our understanding of consciousness continues to evolve, certain experiences, like Near-Death Experiences, challenge traditional views and provide new perspectives on what it means to be conscious. These intriguing experiences have stimulated much debate and are now casting doubt on previously held assumptions about the nature of consciousness. In this section, we will explore some of the latest and most exciting theories that seek to explain the phenomenon of consciousness, including non-local consciousness and panpsychism. Together, these theories paint a fascinating picture of how we might reshape our understanding of the world and our place within it.
Non-local Consciousness
Non-local consciousness is a concept that challenges traditional views of consciousness by suggesting that consciousness exists beyond the individual mind and body. This idea suggests that consciousness is not solely limited to the physical brain and can exist independent of it.
One theory proposes that consciousness arises from interactions at the quantum level within the brain, which could be responsible for the experiences associated with NDEs. According to this theory, consciousness could exist in a non-local state outside of the brain, which would explain why people report profound experiences during NDEs.
Another theory suggests that consciousness is a fundamental aspect of the universe, present in all matter in varying degrees. This theory, known as panpsychism, suggests that all objects, animate and inanimate, possess consciousness to some degree. The human brain, in this theory, would act as a receiver and processor of consciousness rather than as the source of it.
Non-local consciousness has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of consciousness and the nature of reality itself. It challenges both dualistic and materialistic perspectives, suggesting that consciousness is not separate from the physical world but rather an integral part of it.
Further research is needed to fully explore the implications of non-local consciousness and its relationship to NDEs. However, this emerging field offers exciting possibilities for understanding the mysteries of human consciousness.
The concept of non-local consciousness challenges the traditional views of consciousness and offers a new perspective on the nature of reality. As research continues to unfold, we may gain a deeper understanding of this intriguing phenomenon and its potential implications.
For more information on the history and development of NDE research, please see our article on the history of NDE research.
The Theory of Panpsychism
One of the new perspectives on consciousness that challenges traditional views and has gained increasing attention in recent years is the theory of panpsychism. This theory proposes that consciousness is not just exclusive to humans or animals, but is a fundamental property of the universe. According to panpsychism, all physical matter possesses some degree of consciousness, even down to the smallest particles like electrons and protons.
This theory may seem perplexing and counterintuitive at first, as it suggests that even inanimate objects possess some form of consciousness. However, proponents of panpsychism argue that this perspective offers a more comprehensive and plausible explanation for the nature of consciousness than traditional views.
One of the key arguments for panpsychism is the problem of combining subjective experiences with objective physical processes in traditional views of consciousness. This is known as the “hard problem” of consciousness. Panpsychism offers a way to bridge the subjective and objective by positing that consciousness is a fundamental aspect of the objective world.
Table:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Offers a comprehensive explanation for the nature of consciousness. | May seem counterintuitive to some. |
| Solves the “hard problem” of consciousness. | Currently lacks empirical support. |
| Provides an avenue for bridging subjective and objective experiences. | Raises questions about the extent of consciousness in different forms of matter. |
While panpsychism is still a controversial theory and lacks empirical support, it has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of consciousness and the universe as a whole. If consciousness is a fundamental property of the universe, it opens up possibilities for new avenues of research and development in fields such as consciousness science, quantum physics, and philosophy.
Implications and Applications of NDEs
As our understanding of near-death experiences (NDEs) continues to evolve, there’s growing recognition of the significant implications and applications that arise from this phenomenon. NDEs have the potential to have a profound impact on our perception of consciousness and our approach towards end-of-life experiences. In particular, they can be used to enhance our spiritual growth and understanding, as well as to transform the way we provide palliative care. NDEs are instrumental in shaping the way we conduct research and development of consciousness science. The following sections explore these implications and applications of NDEs in greater detail.
Spiritual Growth and Transformation
One of the most significant implications of near-death experiences (NDEs) is their potential for promoting spiritual growth and transformation. Many people who have had NDEs report a greater sense of interconnectedness with others, a decreased fear of death, and an enhanced understanding of the purpose and meaning of life.
Here are some ways in which NDEs have been observed to contribute to spiritual growth and transformation:
- Increased sense of purpose and meaning: Many NDErs come back from their experiences with a renewed sense of purpose and meaning in life. They may feel that they have a specific mission or calling to fulfill, or simply a deeper appreciation for the richness and beauty of life itself.
- Greater openness to spiritual and religious ideas: NDEs often involve encounters with divine or supernatural beings, which can greatly influence a person’s beliefs about religion and spirituality. Many NDErs become more open-minded and accepting of different spiritual traditions and may even integrate aspects of various religions into their own personal belief systems.
- Decreased fear of death: Because many NDErs report feeling a sense of peace and love during their experiences, they may be less afraid of death and what happens after we die. This can lead to a greater acceptance of mortality and a more positive outlook on life.
- Increased empathy and compassion for others: NDEs often involve a sense of interconnectedness with all living things, which can lead to a greater sense of empathy and compassion for others. NDErs may become more motivated to help others and to work towards creating a more just and caring world.
While some skeptics may argue that these changes in attitude and behavior are simply the result of a psychological phenomenon, many NDErs report that their experiences were real and transformative. In fact, research has shown that those who have had NDEs are often more psychologically healthy and resilient than those who have not.
The potential for spiritual growth and transformation is one of the most intriguing and inspiring aspects of NDEs, and further research in this area is sure to yield fascinating insights into the nature of consciousness and the human experience.
Palliative Care and End-of-Life Experiences
One important implication of NDEs is in palliative care and end-of-life experiences. Patients who have been diagnosed with terminal illnesses often experience anxiety and fear, and NDEs have shown to alleviate these negative emotions. Research has found that patients who have had NDEs have a more positive outlook on death, and therefore are less likely to experience depression and anxiety in their final days.
Healthcare providers who have an understanding of NDEs can use this knowledge to better support dying patients. By acknowledging and discussing these experiences, patients who have had NDEs are able to find comfort in knowing that their experiences are valid and accepted.
In addition, NDEs can also help healthcare providers identify patients who may require additional emotional and spiritual support. Patients who have had NDEs often report feelings of transcendence, love, and peace. Recognizing these experiences may allow healthcare providers to tailor their care to meet the unique emotional and spiritual needs of these patients.
Overall, incorporating knowledge of NDEs into palliative care can lead to a more holistic approach to end-of-life care. By addressing not only the physical needs of the patient, but also the emotional and spiritual needs, patients are able to find a sense of peace and comfort during the dying process.
| Implications and Applications of NDEs | |
|---|---|
| Palliative Care and End-of-Life Experiences | Patients who have had NDEs have a more positive outlook on death, and therefore are less likely to experience depression and anxiety in their final days. Healthcare providers who have an understanding of NDEs can use this knowledge to better support dying patients. |
| NDEs can also help healthcare providers identify patients who may require additional emotional and spiritual support. Combining physical, emotional and spiritual support helps in the patient’s holistic approach at end-of-life. |
Research and Development of Consciousness Science
Research and development of consciousness science is a relatively new area of study that has emerged in response to the challenge that NDEs pose to traditional views of consciousness. Researchers in this field aim to develop a clearer understanding of the nature of consciousness and its relationship to the brain and physical reality.
To achieve this, researchers are conducting studies on people who have had NDEs to determine the effects of these experiences on their consciousness. They are also exploring the use of different tools and techniques, such as meditation and spiritual practices, to induce altered states of consciousness that can help in understanding the nature of consciousness.
Some scientists are also developing new theories and frameworks for understanding consciousness beyond the traditional views of dualism and materialism. These new perspectives include non-local consciousness, which proposes that consciousness exists beyond the physical body and brain, and the theory of panpsychism, which suggests that consciousness is a fundamental aspect of the universe and all matter.
The development of consciousness science has practical applications in various fields. For example, this research can be helpful in improving the care and experiences of people at the end-of-life stage. Palliative care providers can use the insights gained from consciousness studies to offer spiritual and emotional support to their patients.
The development of consciousness science can also lead to new approaches in the treatment of mental health disorders. For instance, studies have found that practices like meditation and breathwork can promote positive changes in the brain and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Research and development in consciousness science provide an important opportunity to explore and expand our understanding of the nature of consciousness, as well as its implications and applications in various fields of life.
Conclusion
After exploring the phenomenon of near-death experiences and its challenges to traditional views of consciousness, it becomes clear that our understanding of consciousness is far from complete. While dualism and materialism have long been prevalent, they fail to fully account for the complexities and experiences of consciousness, as highlighted by NDEs.
The theories of non-local consciousness and panpsychism, although relatively new and still being explored, offer fresh perspectives that acknowledge the interconnectedness of all things and the potential for consciousness to exist beyond the confines of the physical body. These theories may provide a more comprehensive understanding of consciousness that aligns with the experiences reported by individuals who have had an NDE.
NDEs also have significant implications for spiritual growth and transformation, palliative care, and the research and development of consciousness science. As more research is conducted and people continue to share their experiences, we may discover new ways to enhance our understanding and application of consciousness in our daily lives and in various fields.
In conclusion, NDEs challenge us to question our existing beliefs and to expand our understanding of consciousness beyond traditional views. They offer a unique glimpse into the mysteries of consciousness and the interconnectedness of all things. As we continue to explore the implications of NDEs and embrace new perspectives, we may unlock the full potential of consciousness and the transformative power it holds.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a near-death experience (NDE)?
An NDE is a subjective experience that occurs when a person is on the brink of death or has been resuscitated after being clinically dead.
What are the common components of NDEs?
The common components of NDEs include an out-of-body experience, passage through a tunnel or void, encountering a bright light, a sense of peace and joy, encountering deceased loved ones, and a life review.
Do all people who are close to death have an NDE?
No, not all people who are close to death have an NDE. It is estimated that between 10-20% of people who are close to death have an NDE.
Can NDEs be induced by drugs or other means?
While certain drugs or physiological factors can produce experiences that resemble NDEs, true NDEs are typically spontaneous and unpredictable.
What is the traditional view of consciousness?
The traditional view of consciousness is one of either dualism or materialism, with dualism holding that consciousness is a non-physical entity separate from the body, and materialism holding that consciousness is a product of the brain and nervous system.
What is non-local consciousness?
Non-local consciousness refers to the idea that consciousness is not confined to the brain or body, but rather encompasses a larger, interconnected field of consciousness that exists beyond the individual self.
What is panpsychism?
Panpsychism is the philosophical belief that consciousness is a universal property of all matter, from subatomic particles to the largest structures in the universe.
Can NDEs lead to spiritual growth and transformation?
Yes, it is often reported that NDEs can lead to spiritual growth and transformation, as individuals come away from the experience with a greater sense of connection to others and the universe, and a decreased fear of death.
What is the role of NDEs in palliative care and end-of-life experiences?
NDEs can provide comfort and a sense of peace for individuals nearing the end of life, as well as their loved ones and caregivers.
What are the implications of NDEs for consciousness science?
NDEs challenge traditional views of consciousness and can provide insights into the nature of consciousness and the mind-body relationship, leading to new avenues of exploration and research in consciousness science.