We often find ourselves pondering the profound nature of our dreams, questioning their significance and searching for clues to unlock their deeper meanings. Throughout history, dreams have been a subject of fascination and intrigue, sparking both philosophical contemplation and scientific exploration. ‘Life is But a Dream’ encapsulates the enigmatic essence of these nocturnal visions, urging us to delve into the mysteries of our subconscious mind. In this comprehensive article, we embark on a journey to unravel the hidden symbolism, interpret the messages, and understand the complexities that lie within the realm of dreams. Join us as we explore the rich tapestry of dream interpretation, from ancient beliefs to modern scientific insights, peering into the realm of the unconscious and unlocking the secrets that lie beneath the surface of our slumbering minds.
The Concept of Dreams
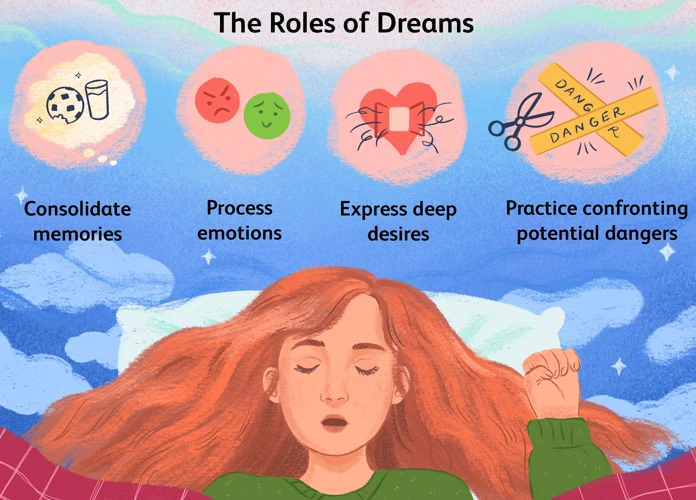
Dreams, captivating and mysterious, have fascinated and perplexed humankind throughout the ages. They are nocturnal reflections of our subconscious mind, transporting us to ethereal realms where reality intertwines with imagination. Across different civilizations and cultures, dreams have been bestowed with varying meanings and interpretations. From the ancient Egyptians who believed dreams were messages from the divine realm to the Greek philosopher Aristotle who considered dreams to be a release of pent-up emotions, the concept of dreams has evolved over time. In the realm of science, the study of dreams has progressed with theories on their purpose and significance. Sigmund Freud, the pioneering psychoanalyst, proposed that dreams are a manifestation of repressed desires and unresolved conflicts, allowing the unconscious mind to communicate with the conscious. The symbolism and meanings embedded within dreams have long captivated humanity, driving individuals to seek understanding and unravel the mysteries of their sleeping visions. (Link: What Does It Mean When a Dead Person Calls Your Name in a Dream?)
1. Dreams Through History
Throughout history, dreams have played a significant role in shaping cultures and belief systems. In ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia, dreams were seen as messages from the gods, offering guidance and insight. The Egyptians even documented their dreams on papyrus, believing that they held prophetic meaning. In Greek and Roman cultures, dreams were seen as a means of communication with the divine, with temples and sanctuaries dedicated to dream interpretation. Native American tribes also held dreams in high regard, considering them to be portals to the spirit world. In more recent times, figures like Sigmund Freud and Carl Jung have contributed to the study of dreams, delving into their psychological significance and symbolism. Today, dream analysis continues to be a fascinating field of study, offering insights into the workings of the human mind. (Link: Dream About Cockroaches)
2. Science of Dream Interpretation
Understanding the science behind dream interpretation provides us with valuable insights into the workings of our subconscious mind. Scientists have made significant progress in unraveling the mysteries of dreams through various approaches. One such approach is neuroimaging, which allows researchers to observe brain activity during sleep and analyze the regions responsible for dreaming. This enables them to identify patterns and connections between neural processes and dream content. Another scientific method involves conducting surveys and experiments to gather data about dreams and their common themes. By examining large sample sizes and applying statistical analysis, scientists can identify patterns and trends in dream content and establish associations between specific dreams and psychological states. Additionally, psychologists have developed frameworks and theories for interpreting dreams, such as Carl Jung’s concept of archetypes and their influence on dream symbols. This scientific exploration of dream interpretation not only provides us with a deeper understanding of the inner workings of the human mind but also offers practical tools for individuals to gain insight into their dreams and their significance. (Link: Eagle in Dream Meaning)
Interpreting ‘Life is But a Dream’

Interpreting the phrase “Life is But a Dream” requires a multifaceted exploration, drawing from various philosophical and psychological perspectives. Philosophers view this phrase as a reflection of the transient and illusory nature of existence. The concept of life being a dream can be traced back to ancient Hindu and Buddhist philosophies, where the material world is considered an illusion. In modern times, existentialists like Friedrich Nietzsche and Jean-Paul Sartre suggest that life is subjective, and our perception shapes our reality. From a psychological standpoint, “Life is But a Dream” can be interpreted through the lens of our unconscious mind. Sigmund Freud believed that dreams serve as a window into our deepest desires and fears, allowing us to explore repressed thoughts and hidden meanings. Carl Jung expanded this perspective by introducing the idea of the collective unconscious, a shared pool of symbolic imagery that connects us to universal archetypes. By unraveling the intricate layers of meaning behind this enigmatic phrase, we gain insights into the nature of reality and the complexities of our human existence.
1. Philosophical Perspectives
In exploring the philosophical perspectives on dream interpretation, we delve into the profound inquiries of renowned thinkers throughout history. Plato, in his allegory of the cave, compared dreams to the illusory nature of perceptions and reality. He believed that dreams provided glimpses into a higher realm of truth and knowledge. René Descartes, the influential French philosopher, pondered the distinction between dreams and waking life, asking how we can truly differentiate between the two. German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche proposed that dreams reveal the innermost desires and aspirations of an individual, exposing their true nature. These philosophical perspectives collectively demonstrate the fascination and contemplation surrounding dreams, highlighting the endless possibilities they present and the profound impact they have on our perceptions of reality.
2. Psychological Interpretations
Psychological interpretations of dreams delve into the intricate workings of the human mind, providing valuable insights into our emotions, fears, and desires. One such approach is Carl Jung’s theory of dream analysis, which explores the idea of the collective unconscious. According to Jung, dreams are not just individual manifestations but also contain symbols and archetypes that are universally shared across cultures. These symbols can represent aspects of our personality, emotions, or experiences. For example, dreaming about a snake may symbolize our hidden fears or repressed instincts. Another prominent psychological interpretation of dreams comes from cognitive psychology, which emphasizes how dreams reflect our cognitive processes and mental states. This perspective suggests that dreams serve as a way for our brain to process information, memories, and emotions. Freudian psychoanalysis also plays a significant role in understanding dreams, focusing on the notion that dreams are a manifestation of our deepest desires and fears. By analyzing dream symbols and uncovering their hidden meanings, psychological interpretations offer valuable insights into the complexities of the human psyche.
The Symbolism of Dreams

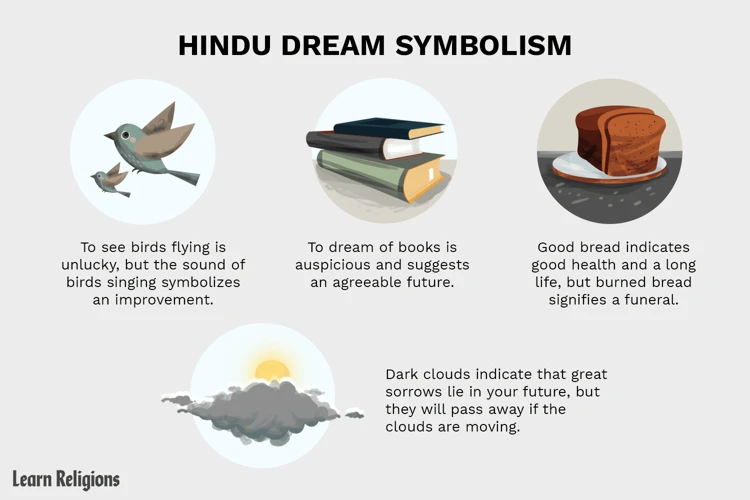
The symbolism of dreams serves as a gateway to understanding the hidden messages and subconscious desires that reside within our sleeping minds. Dreams often present themselves in a symbolic language, where objects, people, or scenarios take on deeper meanings beyond their literal interpretation. Some common dream symbols include water, which represents emotions and the unconscious; snakes, which signify transformation and healing; and flying, which symbolizes a sense of freedom and liberation. These symbols can vary in meaning based on cultural context and personal experiences. Additionally, dreams can also tap into the collective unconscious, a concept introduced by renowned psychologist Carl Jung. This collective unconscious contains archetypes, universal symbols and themes shared by all of humanity across time and cultures, such as the hero, the shadow, and the mother figure. By exploring and decoding the symbolism of our dreams, we gain valuable insights into our innermost thoughts, emotions, and desires, paving the way for personal growth and self-discovery.
1. Common Dream Symbols
Common dream symbols are the enigmatic language of our subconscious mind, communicating hidden messages through vivid imagery. These symbols often carry personal and universal meanings, inviting us to unravel their significance and uncover the truths they hold. Dreams of flying can symbolize a sense of freedom, while dreams of falling may reflect a lack of control or fear of failure. Water in dreams can represent emotions, ranging from calmness to turbulence, and snakes can symbolize transformation or hidden fears. Houses, cars, and even animals hold their own symbolic interpretations within the dream realm. However, it is important to note that the meaning of these symbols can vary based on personal experiences and cultural associations. Studying common dream symbols can provide a framework for understanding the deeper messages behind our dreams, but it is essential to approach dream interpretation with an open mind and consider the unique context of each dream scenario.
2. Collective Unconscious
The concept of the collective unconscious, proposed by renowned Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung, adds an intriguing dimension to the interpretation of dreams. According to Jung, the collective unconscious is a reservoir of shared archetypes and symbolic imagery that transcend individual experiences. These archetypes, such as the anima, animus, and shadow, serve as universal patterns and themes that are present in the dreams of individuals from all cultures and backgrounds. The collective unconscious suggests that certain dream symbols and themes are deeply ingrained within the human psyche and carry collective meaning. For example, the symbol of a serpent often represents transformation and rebirth in various cultures throughout history. This collective symbolism points to a shared understanding and connection between humanity, bridging gaps of time and culture. By exploring the collective unconscious, we can gain further insight into the deeper layers of symbolism and meaning within our dreams.
Unconscious Desires and Fears
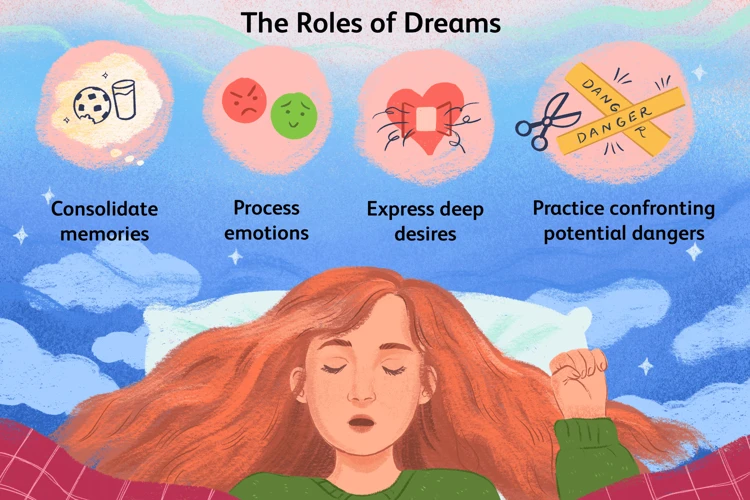
Understanding the realm of dreams requires delving into the depths of our unconscious desires and fears. The concept of the “unconscious” was introduced by Sigmund Freud, who believed that our dreams provide a glimpse into our hidden desires and repressed emotions. According to Freud, dreams have both manifest content, which is the literal storyline of the dream, and latent content, which represents the symbolic meaning behind the dream. Unearthing the latent content involves interpreting the symbols, themes, and emotions present in the dream to uncover the underlying unconscious desires and fears. Freudian analysis suggests that dreams act as a safety valve, allowing the release of repressed desires that are deemed unacceptable in waking life. By analyzing the intricate layers of our dreams, we gain insight into our deep-seated motivations, fears, and unresolved conflicts. This process of self-exploration can lead to personal growth and a better understanding of ourselves. It is through understanding our unconscious desires and fears that we can begin to unravel the complex tapestry of our dreams and decipher the messages they hold.
1. Manifest and Latent Content
Manifest and latent content are essential concepts in Freudian dream analysis, allowing us to delve into the hidden meanings behind our dreams. Manifest content refers to the surface-level content of a dream, the literal events and visuals that we experience while asleep. It is what we consciously remember upon waking up. However, according to Freud, these elements serve as mere disguises for the true underlying message of the dream, known as the latent content. The latent content represents the hidden, symbolic meanings and unconscious desires embedded within the dream. It is through the interpretation of the latent content that the true significance and exploration of our subconscious mind can be realized. By unraveling the symbolic elements and deciphering the latent content of our dreams, we can gain insights into our innermost thoughts, fears, desires, and conflicts, thereby gaining a deeper understanding of ourselves.
2. Freudian Analysis
Freudian analysis delves into the realm of the unconscious mind, unraveling the hidden desires and fears that manifest in our dreams. According to Sigmund Freud, dreams are symbolic expressions of our repressed sexual and aggressive instincts, serving as a gateway to our deepest desires and anxieties. Through the process of dream analysis, Freud believed that one could uncover the latent content, the hidden meaning behind the manifest content of a dream. Symbolism plays a crucial role in Freudian dream interpretation, as objects, actions, and even people in dreams become metaphors for underlying psychological conflicts. For example, a dream about falling may reflect feelings of insecurity or a loss of control in one’s waking life. By unraveling these symbolic representations, Freudian analysis aims to bring repressed thoughts and emotions to the surface, ultimately leading to a better understanding of oneself and the psyche. The exploration of dreams through a Freudian lens provides valuable insights into the complexities of the human mind and how our unconscious desires shape our conscious experiences.
Lucid Dreaming and Control

Lucid dreaming, a phenomenon that combines consciousness and dreaming, offers a gateway to unparalleled exploration and control within the realm of dreams. In a lucid dream, the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming, allowing them to actively participate and manipulate the dream scenario. This state of heightened awareness opens up a world of possibilities, where imagination knows no bounds. Various techniques, such as reality testing and visualization exercises, can be employed to induce lucid dreams. Once in control, individuals can shape their dream narrative, consciously interacting with dream characters and altering the dream environment. Lucid dreaming has been a subject of great interest for both scientific research and personal development. It presents an opportunity for self-discovery, creativity, and even problem-solving. Those who practice lucid dreaming may report enhanced psychological well-being and a deeper understanding of their subconscious mind. The ability to harness the power of lucid dreams offers a unique and exciting avenue for exploring the depths of the human mind. (Link: Eagle in Dream Meaning)
1. Techniques for Lucid Dreaming
To experience the captivating realm of lucid dreaming, where we become aware of and can control our dreams, various techniques can be employed. One popular approach is reality testing, where one regularly questions their surroundings to distinguish between dreams and reality. This helps develop a habit of questioning one’s state of consciousness, increasing the likelihood of becoming lucid during dreams. Another technique is known as the Mnemonic Induction of Lucid Dreams (MILD), which involves setting intentions before sleep and repeating a mantra like “I will be aware that I am dreaming” to enhance self-awareness during dreams. Wake-Induced Lucid Dreaming (WILD) involves maintaining consciousness while transitioning from wakefulness to the dream state, often through meditation or visualization practices. Additionally, keeping a dream journal to record dreams and identify patterns can enhance dream recall and boost the chances of achieving lucidity. By employing these techniques, individuals may cultivate the ability to enter the vibrant and immersive landscape of lucid dreaming.
2. Harnessing Lucid Dreams
Harnessing the power of lucid dreams opens up a realm of possibilities for individuals to explore and control their dream experiences. Lucid dreaming occurs when one becomes aware that they are dreaming while still in the dream state. It offers a unique opportunity to actively participate and manipulate the dream narrative. Various techniques can be employed to induce lucid dreams, such as reality checks, keeping a dream journal, and practicing mindfulness and meditation. One effective technique is the Mnemonic Induction of Lucid Dreams (MILD) method, where individuals repeat a mantra or affirmation before sleep, affirming their intention to become aware within their dreams. Once lucidity is achieved, dreamers can engage in activities impossible in waking life, such as flying, teleportation, or even summoning dream characters for conversation or guidance. Lucid dreaming can also be utilized for personal growth, self-exploration, and creative inspiration. Artists and writers, for example, often seek to tap into their subconscious realms to access new ideas and inspirations. By harnessing the power of lucid dreams, individuals can transcend the boundaries of reality and embark on extraordinary inner journeys of self-discovery and limitless possibilities.
The Power of Dream Journaling
Dream journaling is a powerful tool that allows us to capture and explore the depths of our dreams. Keeping a record of our dreams enhances our ability to recall and analyze them, providing invaluable insights into our subconscious mind. By maintaining a dream journal, we establish a connection with our dream world, acknowledging its significance and giving it the attention it deserves. There are numerous benefits to this practice. Firstly, dream journaling helps improve dream recall, as the act of writing immediately after waking solidifies the memory. Additionally, it enables us to identify recurring patterns and symbols, providing a deeper understanding of our psyche. Maintaining a dream journal can serve as a therapeutic outlet, allowing us to express and process emotions that may have been stirred by the dreams. Techniques for recording dreams can vary, from simply jotting down key elements to writing detailed narratives. Whichever method one chooses, the act of recording dreams holds immense potential for self-discovery and personal growth. Whether it’s a pen and paper, a digital document, or a dedicated dream journal app, finding a medium that suits your style is the key to unlock the transformative power of dream journaling.
1. Benefits of Keeping a Dream Journal
Keeping a dream journal can be a valuable practice that offers a range of benefits for those seeking to explore and understand their dreams more deeply. By documenting dreams on a regular basis, individuals gain several advantages. Firstly, a dream journal serves as a record of dream content, allowing for reflection and analysis of patterns and themes that may arise. It helps in identifying recurring symbols or scenarios, aiding in the interpretation of dreams over time. Secondly, journaling helps improve dream recall, as the act of writing down dreams stimulates memory and strengthens the connection between the conscious and unconscious mind. A dream journal provides a safe space for personal exploration and expression, allowing individuals to engage with their dreams on a deeper level. It can act as a therapeutic tool, aiding in stress reduction, self-reflection, and emotional processing. Lastly, a dream journal acts as a gateway to self-discovery, offering insights into one’s subconscious desires, fears, and unresolved issues. By delving into the depths of their dreams through journaling, individuals can unlock a wealth of information about themselves and their inner world.
2. Techniques for Recording Dreams
Recording dreams can be a valuable practice in gaining insights into our subconscious mind and uncovering patterns and symbolism within our dreamscape. There are various techniques that can aid in effectively capturing the details of our dreams. One approach is to keep a dream journal, a dedicated notebook where one can jot down the vivid imagery, emotions, and events experienced during sleep. By placing a journal by the bedside, it becomes easier to record dreams immediately upon waking, before the details fade away. Another technique is voice recording, where individuals verbally describe their dreams into a voice recorder or a smartphone app. This method allows for a more fluid and expressive capture of the dream, preserving the nuances of the experience. Additionally, sketching or drawing can be used to visually depict dream scenes, symbols, or objects that may be difficult to put into words. This visual representation can provide deeper insights and connections to the subconscious. Whichever method one chooses, the key is to find a technique that resonates and helps in retaining the intricate fragments of the dream world, enabling greater understanding and reflection.
Conclusion
Exploring the profound concept of dreams has revealed the complex tapestry of symbolism, interpretation, and meaning that resides within our sleeping minds. From ancient beliefs to modern scientific insights, we have delved into the depths of our subconscious and uncovered the power and significance of our nocturnal visions. The concept of dreams has evolved throughout history, encompassing philosophical musings and psychological theories that attempt to decipher their messages. Through the study of dream symbols and the examination of our collective unconscious, we have gained a deeper understanding of the hidden meanings and personal significance that dreams hold. Exploring the realm of unconscious desires and fears has allowed us to unravel the layers of manifest and latent content within our dreams, offering insights into our innermost thoughts and emotions. Additionally, the exploration of lucid dreaming has provided a gateway to control and harness the power of our dreams, expanding our comprehension and enabling us to actively participate in these ethereal experiences. Finally, the practice of dream journaling has been unveiled as a valuable tool in capturing and interpreting our dreams, serving as a bridge between the conscious and unconscious mind. By recording and analyzing our dreams, we unlock a treasure trove of personal insights and gain a deeper connection to our inner selves. In conclusion, the realm of dreams offers a rich and captivating landscape for exploration, providing a gateway to self-discovery, personal growth, and a deeper understanding of the human psyche.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What causes dreams?
Dreams are believed to be a result of various factors, including brain activity, emotions, and memories. During sleep, the brain processes information and experiences from the day, which can manifest as dreams.
2. Can dreams predict the future?
While some people claim to have had prophetic dreams, there is no scientific evidence to support the idea that dreams can predict the future. Dreams are generally seen as a reflection of our thoughts, emotions, and experiences rather than precognitive visions.
3. Why do we often forget our dreams?
Forgetting dreams is a common occurrence due to the brain’s processing of information during sleep. As we wake up and shift our focus to the waking world, the dream memories can quickly fade. However, keeping a dream journal and practicing recall techniques can help improve dream memory.
4. Do dreams have hidden meanings?
Dreams can carry symbolic meanings that relate to our thoughts, emotions, and subconscious desires. However, it is important to remember that dream interpretation can vary depending on individual experiences and personal symbolism.
5. Can recurring dreams be significant?
Recurring dreams can hold significant meaning as they often represent unresolved issues or recurring emotions in our lives. Exploring the patterns and themes in recurring dreams can provide valuable insights into our subconscious concerns.
6. Are nightmares a sign of something negative?
Nightmares can be a result of stress, anxiety, or traumatic experiences. They are the mind’s way of processing and confronting challenging emotions. While they can be unpleasant, nightmares can offer opportunities for personal growth and self-reflection.
7. Can lucid dreaming be learned?
Yes, lucid dreaming can be learned through various techniques such as reality checks, meditation, and keeping a dream journal. With practice and dedication, individuals can increase their ability to consciously control and manipulate their dreams.
8. Are there any benefits to analyzing dreams?
Analyzing dreams can offer valuable insights into our inner thoughts, emotions, and conflicts. It can help with self-discovery, problem-solving, and emotional healing. Additionally, understanding dream symbolism can enhance creativity and intuition in waking life.
9. How can I improve dream recall?
To improve dream recall, it is helpful to establish a regular sleep routine, incorporate relaxation techniques before bed, and keep a dream journal by your bedside. Recording any fragments or feelings from your dreams upon waking can aid in strengthening your dream memory over time.
10. Do animals dream?
Research suggests that animals, especially mammals, do experience different stages of sleep associated with dreaming. They may exhibit behaviors such as twitching, vocalizations, and rapid eye movements during sleep, indicating the possibility of dreaming.